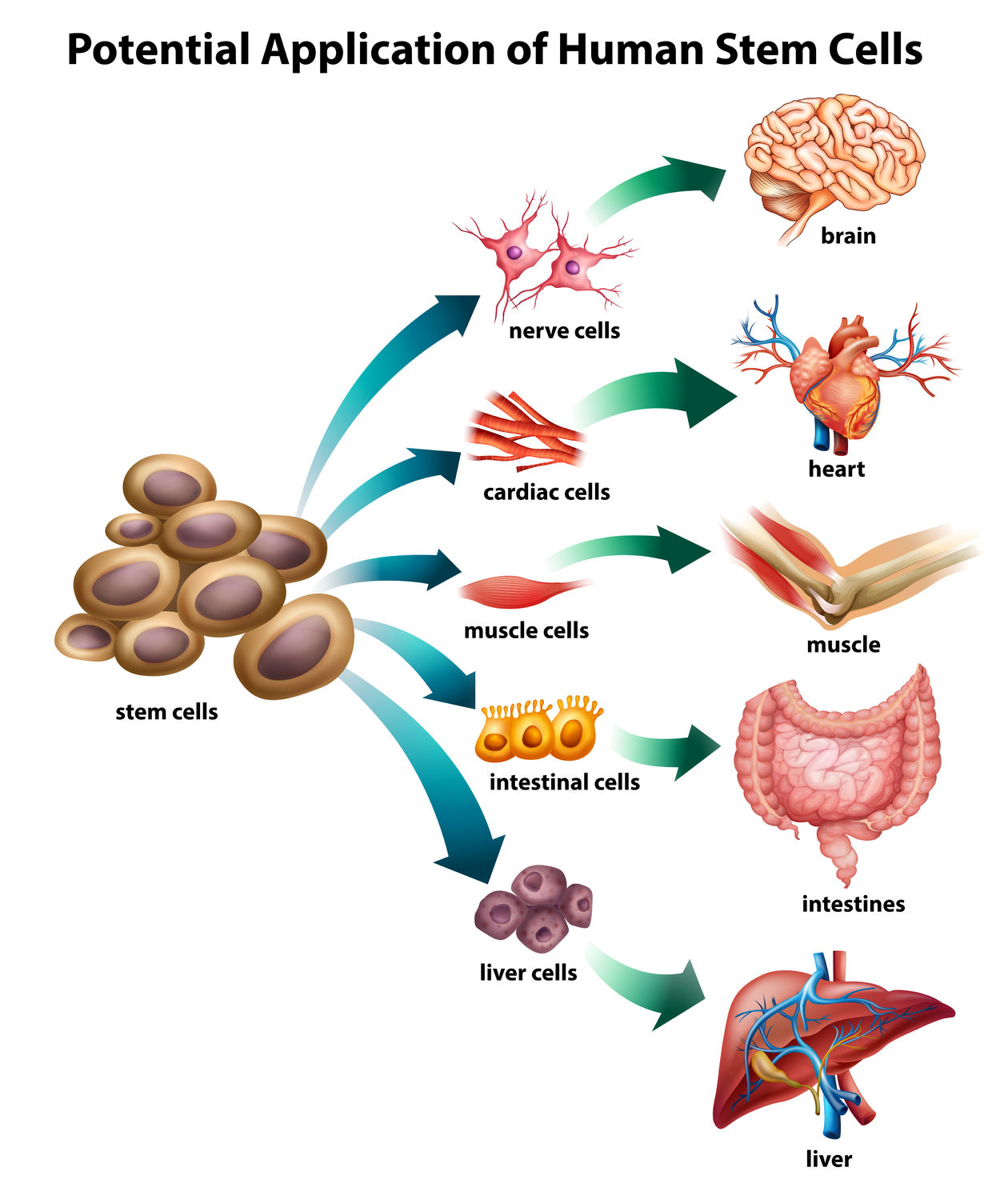
Stem cells are special cells that can self-renew and give rise to different cells with specialized function.
Stem cells can convert to cells of various tissues. Stem cells that are able to convert into every cell in the body are called totipotent. Embryonic stem cells are totipotent. There are also stem cells that can convert into many but not all types of cells. They are called multi-potent. Stem cells from post-natal (after birth) tissues – so called Adult Stem Cells – are multi-potent.
The main source of adult stem cells is the bone marrow (the inner central part of our bone). The bone marrow contains two main populations of stem cells: 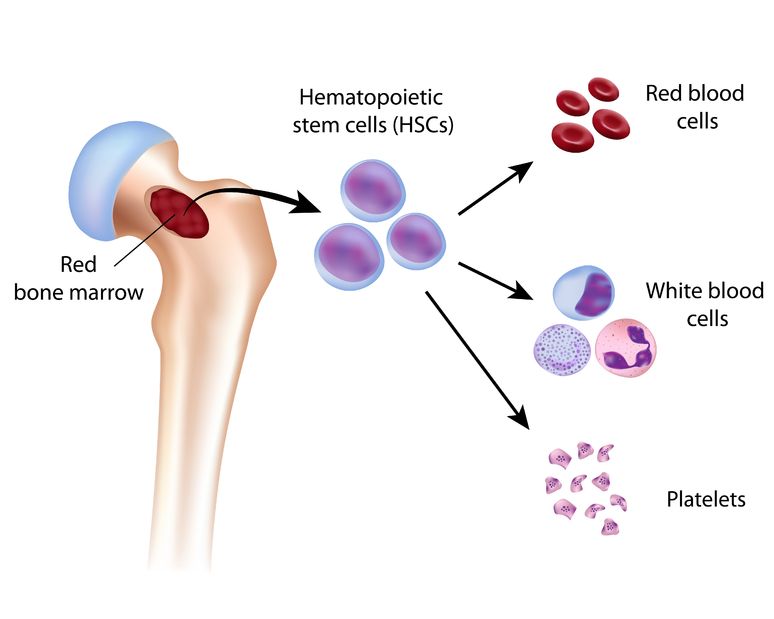 hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells. These cells are crucial in maintaining our health as they continually replace blood and immune cells. These cells are also known to be involved in neovascularisation – the process of building new blood vessels. In addition, these cells are known to convert to various other cells including nerve cells, liver cells, muscle, cartilage and bone cells. In addition, they have many other properties that aid healing.
hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells. These cells are crucial in maintaining our health as they continually replace blood and immune cells. These cells are also known to be involved in neovascularisation – the process of building new blood vessels. In addition, these cells are known to convert to various other cells including nerve cells, liver cells, muscle, cartilage and bone cells. In addition, they have many other properties that aid healing.
Umbilical cord blood is also rich in stem cells which are similar to those from the bone marrow. Even fat contains stem cells; it is especially rich in mesenchymal stem cells.
Bone Marrow Transplant is a procedure where a person’s damaged or destroyed bone marrow is replaced with healthy bone marrow stem cells.
Bone marrow transplant is mainly applicable for treating certain kinds of cancer and has been in practice for more than 50 years. Bone marrow transplants are also applicable in non-cancer conditions such as auto-immune disease (such as Multiple Sclerosis) and genetic disorders (such as beta-thalassemia).
There are two kinds of bone marrow transplants. Autologous and Allogeneic.
The autologous procedure is also called Bone Marrow Rescue. It is applicable when the patient’s bone marrow is not affected by the disease. Firstly, the patient’s own bone marrow is drawn out and saved. Then, high doses of chemotherapy are given, which kills the cancer but also severely affects the bone marrow. The saved bone marrow is then infused back into the patient. This rescues the patient’s bone marrow while getting rid of the cancer. Bone marrow rescue can also be used in auto-immune disease, where high doses of chemotherapy are given to kill immune cells that are self-reactive (which means they are attacking the patient’s own body).
In allogeneic procedure, patient is treated with high doses of chemotherapy and then the bone marrow is replaced by healthy bone marrow obtained from a matching donor.
Stem Cell Banking involves saving of our stem cells for future use.
Stem cells are available in almost all tissues of the body. However, cells from many tissues cannot be accessed. The main sources of stem cells that are easily accessible are bone marrow, umbilical cord and umbilical cord blood, fat, and dental pulp (teeth).
Of these sources, umbilical cord blood is the easiest to source. However, it is available only at the time of birth. Bone marrow stem cells are the gold standard of adult stem cells. Fat is an abundant source of a particular type of cell called mesenchymal stem cell. Dental pulp stem cells may be best suited for neurological problems. Umbilical cord also contains mesenchymal stem cells.
So, how do we save these cells? And more importantly, why do we save the cells?
Cells have to be saved using a special process called cryopreservation. It simply means saving in cold. Cells have to be saved at temeperatures below -150 degrees. Of course, if we simply plunge cells into -150 degrees, cells will freeze to death. Therefore, cryopreservation involves a careful preparation and processing of cells so that they can survive the freezing process.
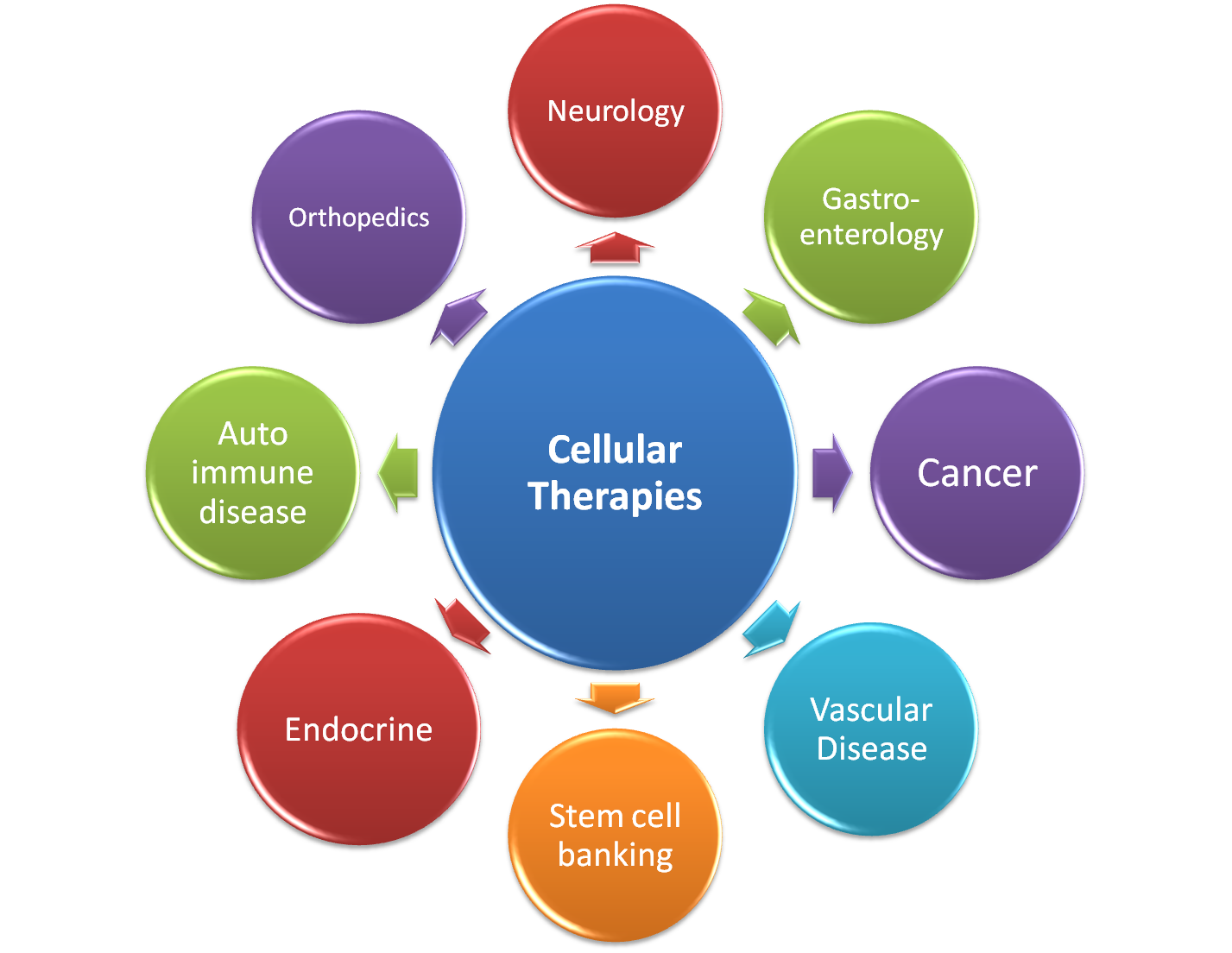
Stem cells can play a major role in Cellular Therapies.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the role of stem cells in healing as they possess properties that promote Renewal, Rejuvenation and Regeneration of damaged tissues.
When you bank your stem cells, they will be available to you whenever you most need them.
Timing is of the essence when treating any disease. Immediate access to your stem cells is critical if you want to use stem cells for treatment. Storing your stem cells when you are healthy will be beneficial since it may not be possible to obtain your stem cells in a timely manner after the onset of disease.
Cellular therapies are based on the use of cells – the basic unit of life.
Regenerative Medicine is a form of cellular therapy that focuses on the regeneration of cunctional tissues. Some forms of cellular therapies have been around for a very long time. Blood transfusion is a form of cell therapy based on cell replacement. Bone marrow transplant is another form of cell therapy utilizing stem cells from the bone marrow.
Advances in our understanding of cells and their function have shown that the inherent properties of cells to heal can be harnessed. In addition to replacing damaged or lost cells, cells can promote healing by:
- Releasing growth factors that promote healing (paracrine effect)
- Modulating the immune system (immune-modulation)
- Reducing inflammation (anti-inflammatory)
- Producing different types of cells with specific function (regeneration)
Stem cells are a special kind of cell that have unique self-renewal properties. Adult stem cells, those obtained from post-natal (after birth) tissues such as blood, bone marrow, fat, umbilical cord and dental pulp, are the main cells used.
Proper understanding and correct implementation is crucial in effectively harnessing the potential of cellular therapies.
Cellular therapies have shown potential in many areas of medicine.