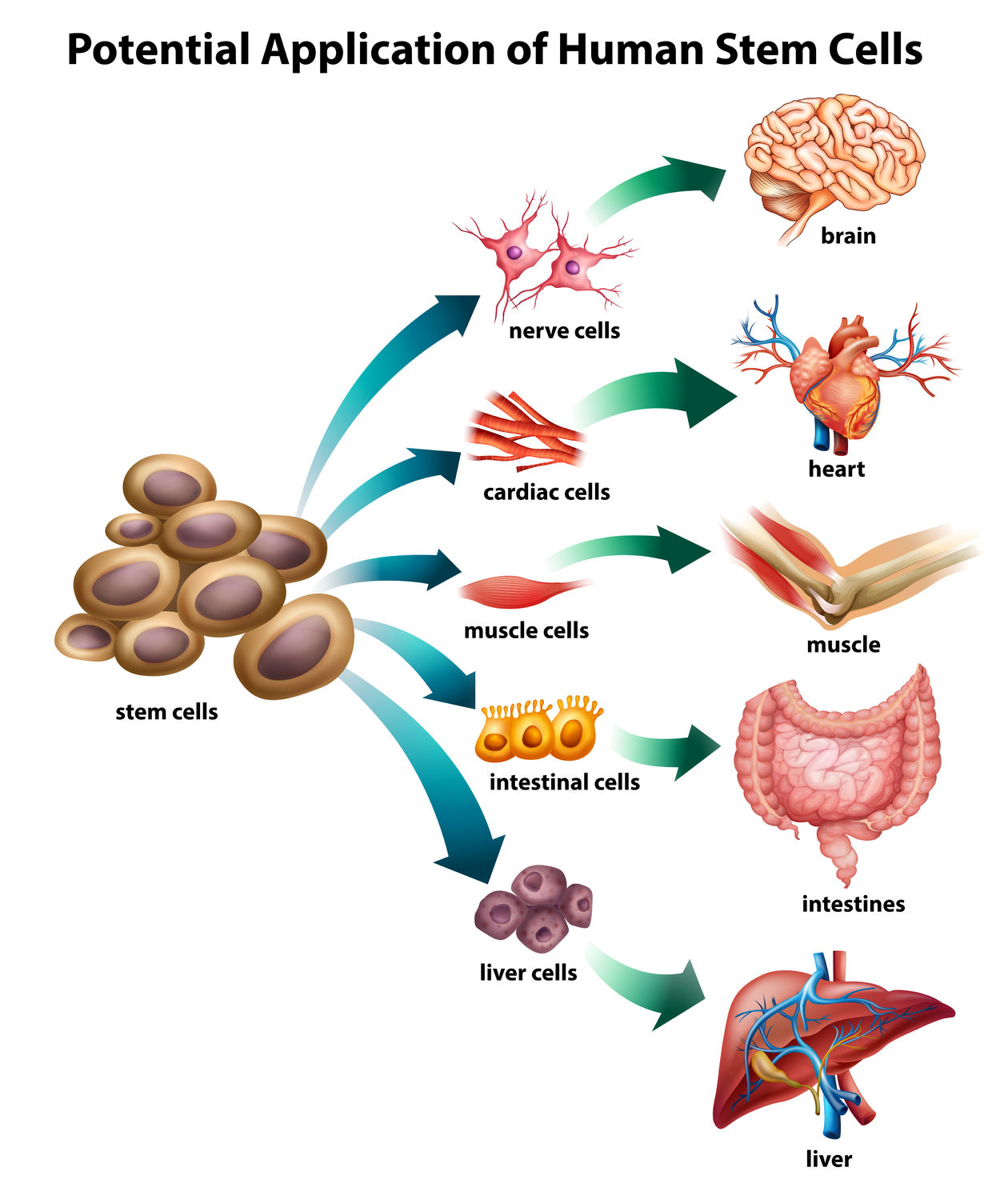
Stem cells are special cells that can self-renew and give rise to different cells with specialized function.
Stem cells can convert to cells of various tissues. Stem cells that are able to convert into every cell in the body are called totipotent. Embryonic stem cells are totipotent. There are also stem cells that can convert into many but not all types of cells. They are called multi-potent. Stem cells from post-natal (after birth) tissues – so called Adult Stem Cells – are multi-potent.
The main source of adult stem cells is the bone marrow (the inner central part of our bone). The bone marrow contains two main populations of stem cells: 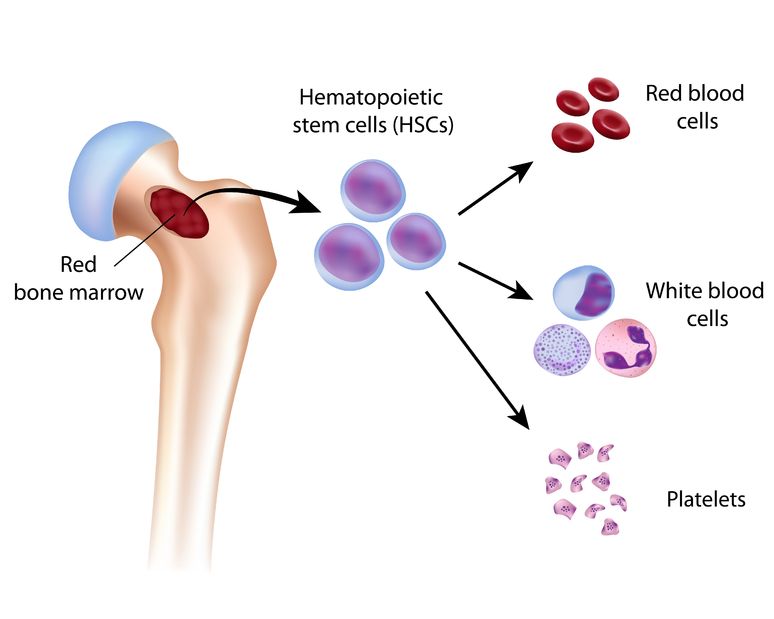 hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells. These cells are crucial in maintaining our health as they continually replace blood and immune cells. These cells are also known to be involved in neovascularisation – the process of building new blood vessels. In addition, these cells are known to convert to various other cells including nerve cells, liver cells, muscle, cartilage and bone cells. In addition, they have many other properties that aid healing.
hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells. These cells are crucial in maintaining our health as they continually replace blood and immune cells. These cells are also known to be involved in neovascularisation – the process of building new blood vessels. In addition, these cells are known to convert to various other cells including nerve cells, liver cells, muscle, cartilage and bone cells. In addition, they have many other properties that aid healing.
Umbilical cord blood is also rich in stem cells which are similar to those from the bone marrow. Even fat contains stem cells; it is especially rich in mesenchymal stem cells.